windows 8
8:59 PM
Run macOS on your PC as a virtual machine
 In the olden days, the only way to run OS X (now called macOS) on a
non-Apple puter was to hack it. In those days, this was a big no-no.
In the olden days, the only way to run OS X (now called macOS) on a
non-Apple puter was to hack it. In those days, this was a big no-no.Fast-forward to today, and things have changed.
Well, sort of.
It still may not be entirely legal to run macOS on your PC, but suddenly it’s very easy to set up. It’s also interesting that despite the very public guides on how to do this, Apple doesn’t seem to care.
So, how do you run a virtual Mac on your Windows or Linux PC?
Easy! You use VirtualBox or VMware. Personally, I switched back to VirtualBox since I seem to have fewer problems with that one, although I was a VMware fan for a short while.
If you’re not familiar with virtualization, here’s a crash course.
What is virtualization?
You have 2 basic options if you want to run more than 1 OS on your puter:Dual-boot or multi-boot:
You set aside a chunk of hard drive space for each OS, and usually you will use GRUB2 to boot into either Windows, or Linux, or whatever. This is relatively complex to set up for newbies, and if things go wrong you will be crying…
Virtual Machines:
This is where you run a program like VirtualBox or VMware in your host OS. So, if you run Windows 7, you just download and install the free VirtualBox for Windows program. When you run it, it allows you to set aside a chunk of your hard drive as a virtual disk. You then use installation media (like a DVD or image file) for your second OS and “virtually install” the guest OS inside Windows – so to speak.
The idea here is that with VirtualBox or VMware, you can run Windows (for example) normally. Inside Windows, you simply run VirtualBox/VMware, and then start your Linux or macOS. You can think of it as running Linux or macOS contained in a window inside Windows itself. If anything goes wrong, you just delete the virtual machine and start over! No dual-boot, no screwing up of Windows, and it’s fairly fast.
With a virtual machine, you can run an entire operating system (including programs on that OS) in the same way that you’d run Chrome or MS Word. Simple! The whole guest OS and all its programs run inside your host OS. Thus, you can run any OS whenever you want, and all you need is a bit of hard drive space. If you need more speedy storage space, check out Samsung’s 850 EVO SSDs
Best of all, it’s all free.
How do I install macOS as a virtual puter?
Piece of cake. You just head on over to YouTube and check out Tech Review’s channel. The latest video shows how to install macOS 10.12 Sierra in VirtualBox:Or in VMware:
Note that you’ll want to click over to YouTube since you’ll need to download the images/files required. The OS images are about 5GB. The links to these files are in the descriptions of the videos.
But, but… Is it legal?
Not really, but yes.For Windows, you’ll need a product key to run even a virtual copy. Linux is generally free to use as you see fit. For macOS, we enter a bit of a grey area…
You can read the macOS license here. It’s pretty clear that you’re only supposed to install macOS on Apple devices.
However, all that’s required to get the macOS image is a Mac – and the Apple Store. Anybody can download it, and there are several publicly-available tools out there for making a bootable USB stick or image that will work anywhere.
Furthermore, if sites like MacWorld are telling you how to install macOS directly on a PC, and Apple doesn’t sue their pants off, then you’re probably safe using a virtual copy… unless you’re afraid that the ghost of Steve Jobs and his army of zombie lawyers are gonna come after you!
And let’s face it: With an estimated 8.5% market share in the OS wars, Apple is playing second fiddle to Windows. It can only benefit Apple to NOT go after people who do this, because maybe they’ll decide it’s worth getting a Mac when they’ve had enough of Windows 10.

And for people like me, it’s very handy to have real macOS running real Safari to test web sites and such!





 If you’ve ever installed multiple operating systems on your computer,
you know what a severe pain it can be when something goes wrong. Even
removing one of your multiple OSes can be a hassle when bootloaders get
all screwed up.
If you’ve ever installed multiple operating systems on your computer,
you know what a severe pain it can be when something goes wrong. Even
removing one of your multiple OSes can be a hassle when bootloaders get
all screwed up. So you get Windows 10. You share your media libraries so other users
on your network can see and play your music from Windows Media Player on
their own puters.
So you get Windows 10. You share your media libraries so other users
on your network can see and play your music from Windows Media Player on
their own puters. The
The 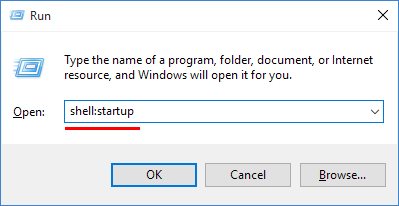
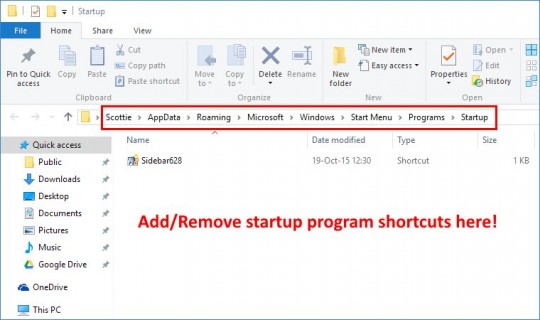
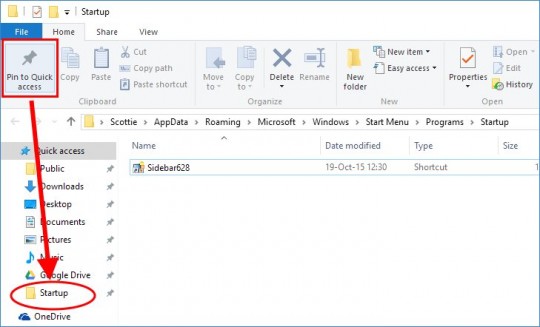
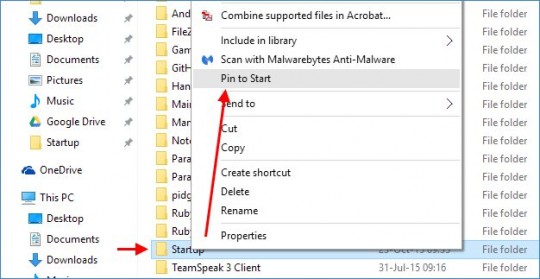

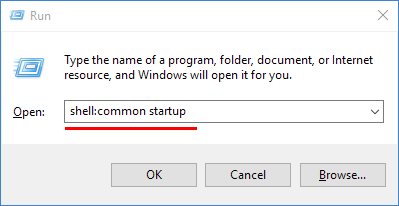
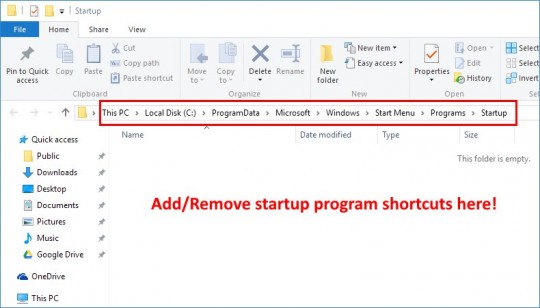
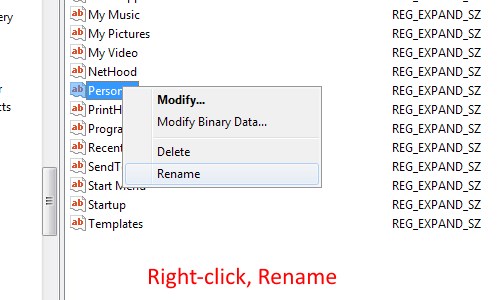
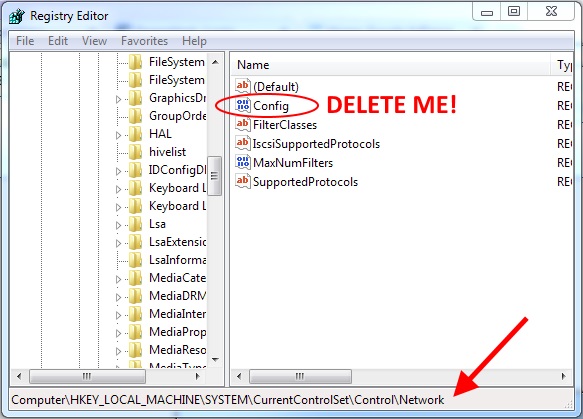
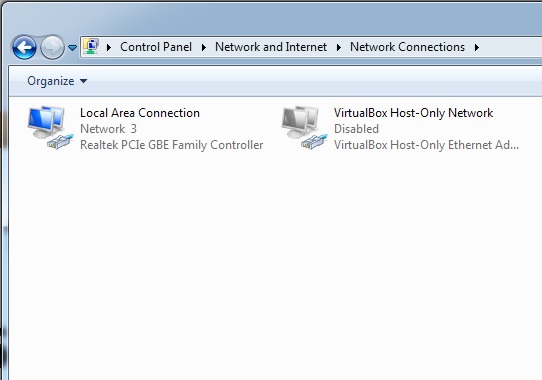
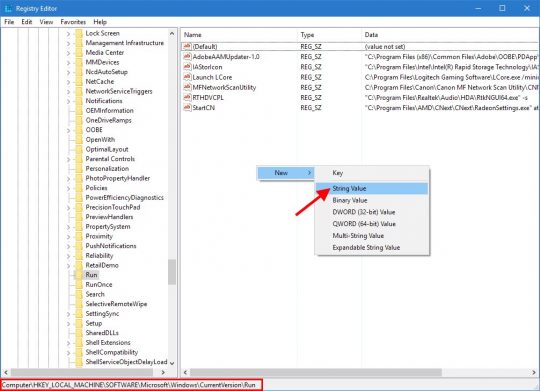
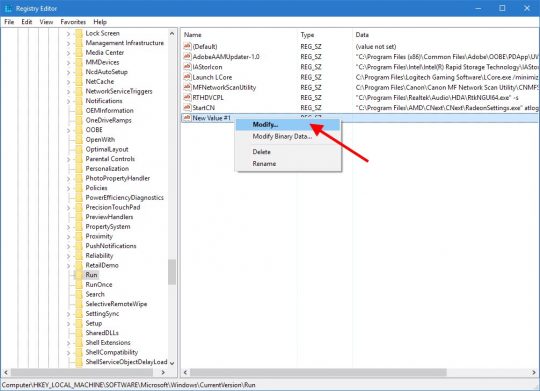
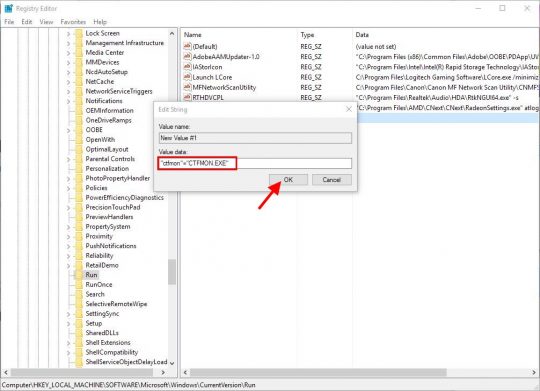
 One of the most common problems I’ve seen is missing or “disappeared” network icons in Windows 7.
One of the most common problems I’ve seen is missing or “disappeared” network icons in Windows 7.
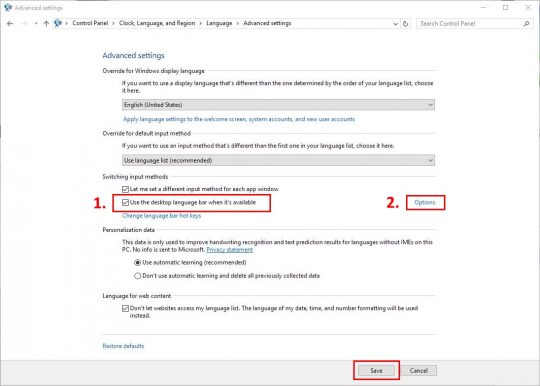
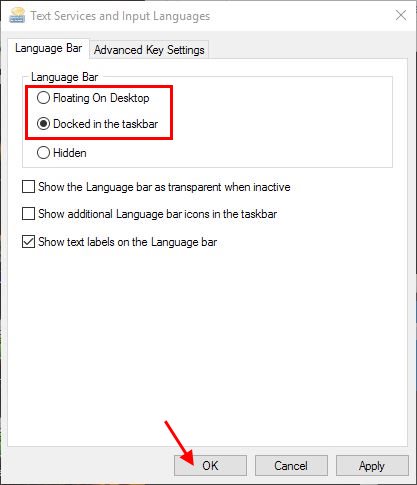
 If you speak more than one language, then you probably also write in more than one language.
If you speak more than one language, then you probably also write in more than one language.
 There are many things to love about Windows 7. It truly is “Vista done right”, sad as that may be. But it ain’t perfect.
There are many things to love about Windows 7. It truly is “Vista done right”, sad as that may be. But it ain’t perfect. This is one of those Windows tricks that you probably didn’t even know existed.
This is one of those Windows tricks that you probably didn’t even know existed.